Understanding Brain Aneurysms
Understanding Brain Aneurysms
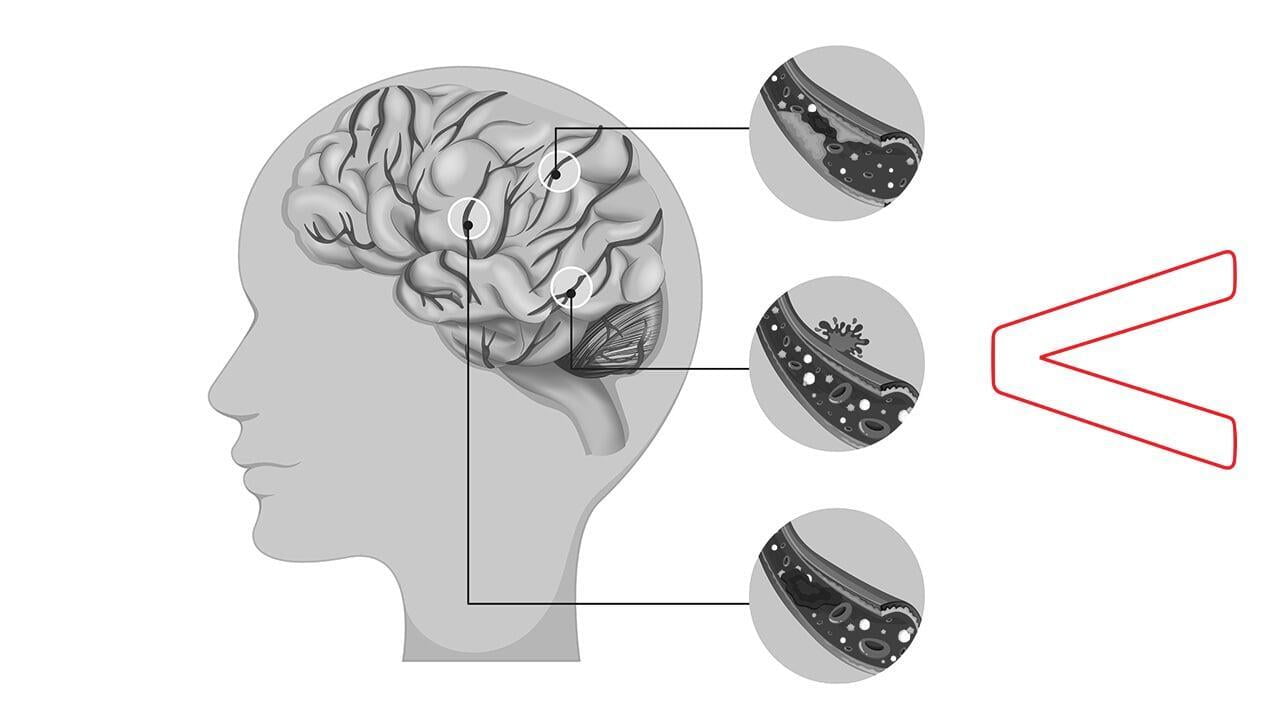
Introduction
Introduction
A brain aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm or intracranial aneurysm, is a critical medical condition that involves a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel in the brain. It often resembles a berry hanging on a stem and can occur at any age. While most brain aneurysms aren't immediately dangerous, they can pose significant risks if they rupture, leading to life-threatening complications such as hemorrhagic strokes.
This article aims to provide a detailed understanding of brain aneurysms, including their types, symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnosis, and treatment options. Additionally, we'll explore the role of RxSaveZ in providing expert advice and supporting patients through this challenging journey.
Types of Brain Aneurysms
Types of Brain Aneurysms
Brain aneurysms can be classified into different types based on their appearance and causes. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment and management approach. Here are the three primary types of brain aneurysms:
Saccular Aneurysm (Berry Aneurysm): This is the most common type of brain aneurysm. It is characterized by a round, blood-filled sac that protrudes from the main artery or one of its branches. The term "berry aneurysm" comes from its resemblance to a small berry hanging from a vine. Saccular aneurysms typically form at the base of the brain and are more prone to rupture.
Fusiform Aneurysm: This type of aneurysm causes a uniform bulging on all sides of the artery. Unlike saccular aneurysms, fusiform aneurysms are less likely to rupture but can still pose risks if they grow large.
Mycotic Aneurysm: This type of aneurysm is caused by an infection, weakening the artery wall. It is less common but can occur when infections affect the arteries in the brain.
Saccular Aneurysm (Berry Aneurysm): This is the most common type of brain aneurysm. It is characterized by a round, blood-filled sac that protrudes from the main artery or one of its branches. The term "berry aneurysm" comes from its resemblance to a small berry hanging from a vine. Saccular aneurysms typically form at the base of the brain and are more prone to rupture.
Fusiform Aneurysm: This type of aneurysm causes a uniform bulging on all sides of the artery. Unlike saccular aneurysms, fusiform aneurysms are less likely to rupture but can still pose risks if they grow large.
Mycotic Aneurysm: This type of aneurysm is caused by an infection, weakening the artery wall. It is less common but can occur when infections affect the arteries in the brain.
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms
Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms
The symptoms of brain aneurysms can vary depending on whether the aneurysm is ruptured or unruptured. It's essential to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
Here's what to look for:
Ruptured Aneurysm Symptoms
A ruptured brain aneurysm is a medical emergency. The primary symptom is a sudden and severe headache, often described as the worst headache a person has ever experienced. Additional symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm can include:
Nausea and vomiting
Stiff neck
Blurred or double vision
Sensitivity to light
Seizures
A drooping eyelid
Loss of consciousness
Confusion
If someone experiences these symptoms, immediate medical attention is critical. A ruptured aneurysm can lead to life-threatening complications, and timely intervention is key to improving the chances of survival.
Unruptured Aneurysm Symptoms
Unruptured brain aneurysms often go unnoticed because they don't always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are typically associated with larger aneurysms pressing against brain tissue or nerves. Symptoms of an unruptured brain aneurysm may include:
Pain above and behind one eye
A dilated pupil
A change in vision or double vision
Numbness on one side of the face
It's important to note that many brain aneurysms are discovered incidentally during imaging tests conducted for other reasons. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes and Risk Factors
Brain aneurysms form due to the weakening of artery walls, which can occur for various reasons. Although aneurysms can appear anywhere in the brain, they are most common at forks or branches in arteries where the vessel walls are naturally weaker. The following are some common causes and risk factors for brain aneurysm formation:
Causes
Thinning Artery Walls: The primary cause of brain aneurysms is the thinning of artery walls. This can occur due to genetic factors or external influences.
Weakness at Artery Forks: Aneurysms tend to form at artery forks or branches, where the vessel walls are naturally weaker.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing brain aneurysms or experiencing aneurysm ruptures. These risk factors include:
Age: While brain aneurysms can occur at any age, they are more common in adults between the ages of 30 and 60.
Gender: Women are more prone to brain aneurysms than men.
Cigarette Smoking: Smoking weakens artery walls and is a significant risk factor for both the formation and rupture of brain aneurysms.
High Blood Pressure: This condition can weaken arteries, increasing the likelihood of aneurysm formation and rupture.
Drug Use: Particularly cocaine use, which raises blood pressure and can lead to infection when used intravenously, potentially causing a mycotic aneurysm.
Heavy Alcohol Use: Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of brain aneurysms.
Inherited Connective Tissue Disorders: Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome weaken blood vessels.
Polycystic Kidney Disease: This inherited disorder results in fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys and may increase blood pressure.
Narrow Aorta: Known as coarctation of the aorta, this condition can also increase the risk of brain aneurysms.
Brain Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): A condition where arteries and veins in the brain are tangled, affecting blood flow.
Family History: Having family members with brain aneurysms increases your risk, especially if two or more first-degree relatives have had a brain aneurysm.
Some aneurysms may occur due to head injuries or certain blood infections. Understanding these risk factors can help identify those at higher risk and guide preventive measures.
Complications of a Ruptured Brain Aneurysm
Complications of a Ruptured Brain Aneurysm
When a brain aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to severe complications that require immediate medical intervention. These complications can have life-threatening consequences and significantly impact a person's quality of life. Here are some of the common complications of a ruptured brain aneurysm:
Re-bleeding
An aneurysm that has ruptured or leaked is at risk of bleeding again, known as re-bleeding. Re-bleeding can cause additional damage to brain cells and may increase the risk of severe complications or death.
Narrowed Blood Vessels (Vasospasm)
After a brain aneurysm ruptures, blood vessels in the brain may contract and narrow, leading to vasospasm. This narrowing can cause an ischemic stroke, where there's limited blood flow to brain cells. Vasospasm can cause additional damage and loss of brain function.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus occurs when there's a buildup of fluid within the brain. This often happens after a ruptured brain aneurysm, as the blood can block the movement of fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This buildup increases pressure within the brain, potentially causing further damage.
Change in Sodium Level
Bleeding in the brain can disrupt the balance of sodium in the blood, leading to swelling of brain cells and permanent damage. This complication can result from damage to the hypothalamus, a crucial area near the base of the brain.
If a brain aneurysm ruptures, immediate medical attention is crucial to address these complications and minimize damage. This is where RxSaveZ comes in, providing quick access to medical experts and coordinating care to ensure patients receive the best treatment and support.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
While some factors contributing to brain aneurysms are beyond our control, there are lifestyle changes and preventive measures that can reduce the risk of aneurysm formation and rupture. Here are some of the preventive steps you can take:
Quit Smoking
Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for brain aneurysms. If you smoke, consider seeking support to quit. RxSaveZ offers resources and support to help patients overcome smoking addiction.
Control Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is another critical risk factor. Working with your healthcare provider to manage and control blood pressure can reduce the risk of aneurysm formation and rupture.
Avoid Heavy Alcohol Use
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and contribute to the risk of brain aneurysms. Limit alcohol intake to reduce this risk.
Maintain a Healthy Diet and Exercise
A balanced diet and regular exercise can help control blood pressure and promote overall cardiovascular health. RxSaveZ offers guidance on healthy lifestyle choices to support patients on their health journey.
Avoid Recreational Drug Use
Drug use, particularly cocaine and other stimulants, increases the risk of brain aneurysms and other health complications. If you need assistance quitting drug use, seek professional support.
Taking these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of brain aneurysm-related complications. RxSaveZ is here to help you make informed choices and access the resources needed for a healthier lifestyle.
Diagnosis and Screening
When it comes to diagnosing brain aneurysms, early detection is crucial to prevent severe complications. Several imaging tests and diagnostic procedures are used to detect brain aneurysms. Here's an overview of the most common methods:
CT Scan
A CT (computed tomography) scan is a specialized X-ray that creates detailed images of the brain. It is often the first test used to detect bleeding in the brain or another type of stroke. A CT angiogram, which involves injecting dye to visualize blood flow, can provide more detailed images of the arteries in the brain.
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, involves drawing cerebrospinal fluid from the lower back with a needle. This test can help determine if there's bleeding in the brain, indicating a ruptured aneurysm.
MRI and MR Angiography
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. MR angiography provides detailed images of the arteries, allowing detection of the size, shape, and location of an unruptured aneurysm.
Cerebral Angiogram
A cerebral angiogram, also known as a cerebral arteriogram, involves inserting a catheter into a large artery (usually in the groin or wrist) and threading it into the brain's arteries. A special dye is injected, allowing detailed X-ray images to detect aneurysms.
These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals determine the presence and severity of brain aneurysms. RxSaveZ assists patients in accessing these diagnostic tests and guides them through the process of obtaining accurate diagnoses and second opinions.
Treatment of Brain Aneurysms
Treatment of Brain Aneurysms
The treatment of brain aneurysms depends on whether the aneurysm is ruptured or unruptured, as well as the aneurysm's size, location, and overall appearance. Here are the most common treatment options:
Surgical Clipping
Surgical clipping involves removing a section of the skull to access the aneurysm. A tiny metal clip is placed on the neck of the aneurysm to stop blood flow into it. This method is highly effective, and once clipped, the aneurysm typically doesn't return.
Endovascular Coiling
Endovascular coiling is a less invasive procedure where a catheter is threaded through the artery to the aneurysm. A spiral-shaped coil is inserted to prevent blood flow into the aneurysm, causing it to clot and ultimately destroying it. This method carries a risk of the aneurysm reappearing, requiring follow-up imaging tests.
Flow Diversion
Flow diversion involves placing a stent in the artery to divert blood flow away from the aneurysm, allowing the body to heal and seal the aneurysm over time. This method is particularly useful for larger aneurysms that can't be treated with other options.
RxSaveZ works with leading neurosurgeons and interventional neuroradiologists to provide expert guidance on treatment options. They help patients make informed decisions and coordinate the necessary medical procedures to ensure the best outcomes.
Rehabilitative Therapy and Support
Rehabilitative Therapy and Support
After a ruptured brain aneurysm, rehabilitative therapy may be required to help patients regain lost skills and function. This therapy can include physical, speech, and occupational therapy. RxSaveZ offers support throughout the rehabilitation process, helping patients access the necessary therapy services and connecting them with support groups and other resources.
Cost of Brain Aneurysm Treatment in India
Cost of Brain Aneurysm Treatment in India
The cost of aneurysm repair surgery in India varies depending on the city and the specific treatment required. Below is a summary of the average cost of aneurysm repair surgery across the top 15 cities in India in Indian Rupees (INR):
New Delhi: Lowest cost: 5,40,000; Average cost: 8,00,000; Highest cost: 11,00,000
Mumbai: Lowest cost: 5,55,000; Average cost: 8,25,000; Highest cost: 11,50,000
Chennai: Lowest cost: 5,60,000; Average cost: 8,50,000; Highest cost: 11,80,000
Bangalore: Lowest cost: 5,75,000; Average cost: 8,60,000; Highest cost: 11,95,000
Hyderabad: Lowest cost: 5,80,000; Average cost: 8,55,000; Highest cost: 11,85,000
Ahmedabad: Lowest cost: 5,60,000; Average cost: 8,60,000; Highest cost: 11,00,000
Nagpur: Lowest cost: 4,90,000; Average cost: 7,00,000; Highest cost: 11,75,000
Kolkata: Lowest cost: 5,60,000; Average cost: 8,60,000; Highest cost: 11,00,000
Pune: Lowest cost: 5,35,000; Average cost: 8,25,000; Highest cost: 11,50,000
Gurgaon/Gurugram: Lowest cost: 5,40,000; Average cost: 8,50,000; Highest cost: 11,75,000
Chandigarh: Lowest cost: 5,50,000; Average cost: 8,55,000; Highest cost: 11,85,000
Jaipur: Lowest cost: 5,55,000; Average cost: 8,60,000; Highest cost: 11,95,000
Noida: Lowest cost: 5,40,000; Average cost: 8,50,000; Highest cost: 11,75,000
Kerala: Lowest cost: 5,65,000; Average cost: 8,60,000; Highest cost: 11,00,000
Goa: Lowest cost: 5,60,000; Average cost: 8,60,000; Highest cost: 11,00,000
RxSaveZ can help patients navigate these costs by providing second opinions, recommending cost-effective treatment options, and assisting with travel and accommodation arrangements. The loyalty program offered by RxSaveZ also provides discounts on medical devices and pharmaceutical products, helping patients save money during their treatment journey.
Disclaimer:
The costs represent a general estimate that includes emergency care, hospitalization, surgery, and rehabilitation.
Variability in costs depends on the type of hospital, severity of injury, length of hospital stay, and specific treatment requirements.
Public hospitals generally offer lower-cost or subsidized treatment, while private hospitals are often more expensive.
For precise estimates, consulting with healthcare providers or insurance representatives is recommended.
Regional economic differences and cost of living can impact the overall costs in each city.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Surgery
Factors Affecting the Cost of Surgery
The cost of surgery can vary widely based on several critical factors. Understanding these factors can help patients and their families anticipate and manage the financial implications of surgery. Below are the primary considerations that impact surgical costs:
1. Type of Surgery
The type of surgical procedure is a significant determinant of cost. Surgeries range from minor to complex, with more complicated procedures typically costing more due to specialized equipment, expertise, and longer operating times.
2. Severity of the Condition
Surgical costs can be influenced by the severity of the patient's condition. More severe or complicated cases often require additional resources, longer hospital stays, and intensive care, all of which increase costs.
3. Hospital or Medical Facility
Costs can differ significantly between hospitals and medical facilities. Public hospitals generally offer more affordable rates, while private hospitals tend to be more expensive due to additional amenities and services.
4. Surgeon's Expertise and Reputation
Highly skilled and renowned surgeons often command higher fees due to their expertise and experience. Surgeons with specialized training in specific procedures may charge more than general surgeons.
5. Location and Region
Geographic location plays a role in surgical costs. Surgeries in major cities or metropolitan areas tend to be more expensive due to higher overheads, cost of living, and demand for healthcare services. Costs may be lower in smaller towns or rural areas.
6. Anesthesia and Medication
The type of anesthesia used during surgery, as well as post-operative medications, can affect the overall cost. General anesthesia usually costs more than local anesthesia, and complex cases may require more extensive pain management.
7. Hospitalization and Recovery
The length of hospital stay and the level of care required during recovery impact costs. Patients who need intensive care or specialized post-operative monitoring typically incur higher expenses.
8. Additional Services
Additional services such as diagnostic tests, imaging, rehabilitation, and physical therapy can increase costs. These services are often necessary for proper diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
9. Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage can significantly affect out-of-pocket costs for surgery. The type of insurance plan, coverage limits, co-pays, and deductibles can determine how much of the cost is covered by insurance.
10. Unforeseen Complications
Complications during or after surgery can lead to unexpected costs. This could include additional surgeries, extended hospital stays, or specialized care to address complications.
Final Thoughts
Given the complexity of factors affecting surgical costs, it's crucial to discuss all potential costs with healthcare providers and insurance representatives beforehand. Understanding these factors helps patients and families make informed decisions and plan for the financial implications of surgery.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Brain aneurysms can be life-threatening if they rupture, but early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding the types, symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options for brain aneurysms is crucial in making informed decisions. RxSaveZ is dedicated to supporting patients through every step of this journey, offering expert advice, second opinions, and assistance in finding the best treatment options at a reasonable cost.
If you suspect you have a brain aneurysm or are at risk, don't hesitate to seek medical attention. Early intervention can save lives and prevent severe complications. Remember, RxSaveZ is here to journey with you and ensure you receive the care and support you need for a successful recovery.

